Cloud Computing is the on-demand availability of Computing systems, Power, data storage, and Applications via the internet with no downtime, without direct active management by the user. On-premises hardware has a flexibility problem, and rigidity can limit usability. cloud computing allows enterprises to get their applications up and running faster, with improved manageability and less maintenance.

The beauty which the cloud solution brings is the limitless potential and flexibility for any organization or IT infrastructure.
One of the key benefits of having a cloud solution is that the hardware and software demand of the user or organization side decreases. The cloud solution is typically defined as a type of computing that relies on sharing resources or a multi-tenant setup rather than having local servers or personal devices to handle the applications. Three major parameters namely infrastructure, virtualization platform, and software are being taken care of.
The beauty of cloud solution is it meets the real-time demand and allow the user or an organization to pay only for what they need or the resource they use. The shared IT infrastructure contains a large pool of resources or servers already built, often virtualization, thus reducing the downtime required for setting up the solution for the user.
The increase in the usage of the internet has ultimately increased the demand for cloud solutions and the pandemic has proved that cloud solutions will be the future for many organizations.” Why to work in a closed environment when one can work at their ease and comfort”. On-premise hardware and software have a lot of flexibility and scalability issues which limits one’s thinking. The beauty which the cloud solution brings is the limitless potential and flexibility for any organization or IT infrastructure.
One of the key benefits of having a cloud solution is that the hardware and software demand on the user or organization side decreases. A cloud solution is typically defined as a type of computing that relies on sharing resources or a multi-tenant setup rather than having local servers or personal devices to handle the applications. Three major parameters namely infrastructure, virtualization platform, and software are being taken care of.
The beauty of cloud solution is it meets the real-time demand and allow the user or an organization to pay only for what they need or the resource they use. The shared IT infrastructure contains a large pool of resources or servers already built, often virtualization, thus reducing the downtime required for setting up the solution for the user.
1) It eliminates the traditional IT administrators to provision and manages to compute resources.
2) Organisation has the flexibility to increase or decrease resource usage as per the requirement or demand.
3) Organisation needs to pay only for the resource that is being utilized.
4) Redundant environment for smooth failover.
5) Migration flexibility to and from the cloud.
6) End-user can access the software or cloud solution from anywhere in the world through the internet.
7) Multi-tenancy allows multiple customers to share the resource using the same infrastructure and at the same time providing data security as well as data privacy.
8) Low-cost management and less maintenance work.
The All-in-one cloud solution provides and delivers cloud computing services including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and monitoring. The cloud solution has a great impact to manage solutions at low cost and with low maintenance. The services are fully managed by a single provider and the end-user only needs a computer and internet access.
The cloud solution will become even more important and more opted solutions in the coming years because of its rapid demand and continued growth of major data centers. Organizations have started implementing cloud solutions by renting datacentres and started avoiding physical servers in their premises which can be of huge costs.
When operating in the cloud, one of the key decisions to make is about which type of architecture to adopt for your business and customer data. This is because choosing cost-effective architecture is key to building profitable SaaS software.
Single-tenant and multi-tenant cloud environments are the options to consider. Both types of architecture have security and privacy implications. There’s also the issue of cost, which differs significantly depending on the architecting model you adopt.
SINGLE TENANT VS MULTI-TENANT – LEARN THE DIFFERENCE
Single Tenant – A single instance of the software and supporting infrastructure serves a single customer. With a single tenancy, each customer has his or her own independent database and instance of the software. Essentially, there is no sharing happening with this option.
Potential benefits of single-tenant include:
• Security: A single customer and a single server is often contained on secure hardware being used by a limited number of people.
• Dependability: With an entire environment dedicated to one client, resources are abundant and available anytime.
• Customization: Control over the entire environment allows for customization and added functionality if desired.
Potential drawbacks of single-tenant:
• Maintenance: Single-tenant typically means more tasks and regular maintenance to keep things running smoothly and efficiently.
• Setup/Management: By comparison, SaaS multi-tenant environments are quick to set up and manage.
• Cost: Single-tenant typically allows for more resources, but at a premium price given that there is only one customer for the entire environment.
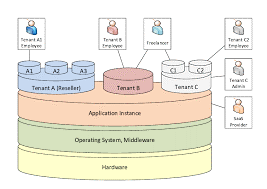
Multi-Tenant – Multi-tenancy means that a single instance of the software and its supporting infrastructure serves multiple customers. Each customer shares the software application and also shares a single database. Each tenant’s data is isolated and remains invisible to other tenants.
Potential benefits of multi-tenant:
• Affordable Cost: Multiple customers mean that the cost for the environment is shared, and those savings (from the SaaS vendor) are typically transferred to the cost of the software.
• Integrations: Cloud environments allow for easier integration with other applications through the use of APIs.
• “Hands-free” Maintenance: The server technically belongs to the SaaS vendor, meaning that a certain level of database maintenance is handled by the vendor, instead of you maintaining the environment yourself.















